Bacteria
Leclercia adecarboxylata
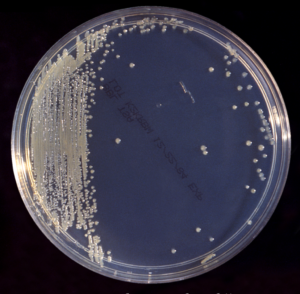
While authorising the urine result – I found that a urine sample from the community has grown Leclercia adecarboxylata. The patient is a young female complaining of increased frequency. The number of organisms in the urine was >100,000 organisms/ml.What is the significance? The bacteria Previously known as Escherichia adecarboxylata, it now belongs to a new genus Leclercia […]
Fusobacterium necrophorum
Bacteria Fusobacterium necrophorum is a Gram-negative, non-motile, non-spore-forming anaerobic pleomorphic bacterium. It may appear in coccobacillus or filamentous forms, which are more common in younger cultures. It is a member of the normal bacterial flora of the oropharynx, genitourinary tract, and gastrointestinal tract. Culture and identification There are 14 species of Fusobacterium, 10 of which […]
Eikenella corrodens
Bacteria: Pathogenicity: Culture and identification: Infection caused by Eikenella: Points to remember Eikenella corrodens is usually susceptible to: Non-susceptible to:
Cronobacter sakazakii: pathogen from infant formula feed
What is Cronobacter sakazakii? Cronobacter sakazakii is a gram-negative bacteria that can cause necrotising enterocolitis, septicaemia, and meningitis in infants, particularly low-birth-weight neonates. It has repeatedly been associated with reconstituted powdered infant formula. It can also cause infection in adults, especially in vulnerable groups like older people. Infection in infants is associated with a high […]
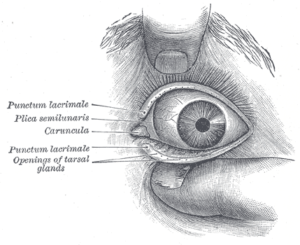
Corynebacterium macginleyi – an under-reported cause of conjunctivitis
Corynebacterium macginleyi (CM) is lipophilic, slow-growing, gram-positive bacteria first described in 1995 and was named after Kenneth McGinley, who made an essential contribution to the field of lipophilic coryneform bacteria. CM has been associated with conjunctivitis and other eye-related infections. It has also been implicated in various non-ophthalmic infections as an opportunistic pathogen. It has […]
Cardiobacterium spp (C hominis, C valvarum)
Bacteria: Microaerophilic, pleomorphic gram-negative bacillus often with swelling of one or both ends and retained crystal violet dye at the poles.It is a part of the normal flora of the nose and throat. Culture and identification: Culture API 20NE – may misidentify it as Pasteurella.MALDI ToF16s rRNA PCR Clinical presentation: Antibiotic susceptibility: Variable susceptibility: Treatment is […]
Capnocytophaga spp.
Capnocytophaga genus belongs to the family Flavobacteriaceae.There are >9 species of Capnocytophaga, which can be divided into two groups – resident of human mouth flora and dog/cat mouth flora. Species found in the human oral cavity C. gingivalis, C. granulosa, C. haemolytica, C. leadbetteri, C. ochracea and C. sputigena Species found in dog/cat oral cavity C. canimorsus and C. cynodegmi Risk factors […]
Brucella
Bacteria There are many Brucella species – not all known to cause human disease. Those known to cause human disease are – B melitensis, B abortus, B suis, B canis and B ceti. Brucella infection is a zoonosis – each Brucella sp is associated with some animal host – Brucella survives in the environment for […]
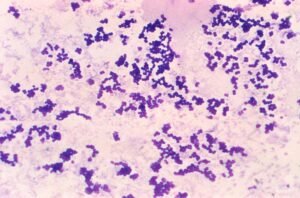
Aerococcus urinae
Aerococcus genus, a firmicute, was first identified in 1953 [Williams, 1953]. Multiple species have been identified since then; not all are human pathogens. Human pathogen Aerococcus viridans, Aerococcus urinae, Aerococcus urinae hominis,Aerococcus christensenii, (2001), Aerococcus sanguinicola. Not human pathogen Aerococcus urinae equi ( or Pediococcus urinae equi), Aerococcus suis, Aerococcus vaginalis. Laboratory identification: Aerococcus is a gram-positive coccus in clusters (like Staphylococcus), alpha-hemolytic on […]