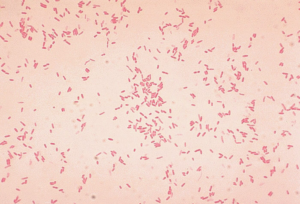
Aerococcus urinae
Aerococcus genus, a firmicute, was first identified in 1953 [Williams, 1953]. Multiple species have been identified since then; not all are human pathogens.
| Human pathogen | Aerococcus viridans, Aerococcus urinae, Aerococcus urinae hominis, Aerococcus christensenii, (2001), Aerococcus sanguinicola. |
| Not human pathogen | Aerococcus urinae equi ( or Pediococcus urinae equi), Aerococcus suis, Aerococcus vaginalis. |
Laboratory identification:
Aerococcus is a gram-positive coccus in clusters (like Staphylococcus), alpha-hemolytic on blood agar and catalase-negative (like Streptococcus).

Differentiation from other organisms:
| Aerococcus is – | |
| Differentiate from Staphylococcus | It is catalase -ve and alpha haemolytic. |
| Differentiate from Streptococcus | It is gram-positive cocci in clusters |
| Differentiate from Pediococcus | It is vancomycin sensitive |
| Differentiate from Gemella | It is catalase-ve |
| Differentiate from Alloioicoccus | It is catalase -ve |
| Differentiate from Helcococcus (Except A christensenii) | It is Asaccharolytic |
Differentiating between Aerococcus sp.
| A viridans | A. urinae | A. christensenii | A. urinae hominis | A sanguinicola | |
| PYR | + | – | – | – | + |
| LAP | – | + | + | – | + |
| Aesculine hydrolysis | + | -/+ | – | + | + |
Identification can be made using automated systems API, 16S rDNA sequence analysis or MALDI ToF. Automated systems may not have all the species in the database.
Clinical presentation
| Aerococcus viridans | Environmental organism – found in soil and air. A rare cause of human disease. Reported to cause – urinary tract infection (UTI), – bacteraemia, – endocarditis and – meningitis |
| Aerococcus urinae | – UTI, – bacteremia/septicaemia, – infective endocarditis. Rarely – – pyelonephritis, – septic arthritis, – discitis, – PD peritonitis, – skin and soft tissue infection has been reported. |
| Aerococcus sanguinicola | – UTI, – bacteremia/septicaemia, – infective endocarditis |
| Aerococcus christensenii | Isolated from the vaginal specimen. ?Bacterial vaginosis |
| Aerococcus urinae hominis | Isolated from urine |
Aerococcus urinae
A urinae is known to cause
- UTI in elderly (median age 75 y; F>M) people with comorbidities (Diabetes Mellitus, malignancy, prostatitis, indwelling catheter etc.)
- bacteraemia (mostly as a complication of UTI),
- endocarditis (a complication of bacteraemia – 1/3rd of bacteraemia cases; poor prognosis)
- and rarely other infections (see chart above).
- The prevalence of these bacteria in the urine is 0.3-4%.
A urinae is often seen in mixed-blood culture with – St aureus, E coli, Actinobaculum schaalii.
Sensitivity and treatment
A urinae is reported to be susceptible to –
| Beta-lactams | It has been reported that Aerococcus urinae is cotrimoxazole resistant. However, Aerococcus urinae can extract folate from the environment like Enterococcus using a high-affinity folate transport binding protein FolT. The thymidine or folate-containing culture media used to test the susceptibility may alter the result. In vivo, the concentration of folate in the urine may depend upon the folate intake. Hence the outcome of the treatment with cotrimoxazole could be unpredictable. |
| Glycopeptide | Susceptible |
| Linezolid | Susceptible |
| Nitrofurantoin | Susceptible |
| Chloramphenicol | Susceptible |
| Rifampicin | Susceptible |
| Quinolone | Many strains are resistant. Levofloxacin is better than Ciprofloxacin |
| Cotrimoxazole | It has been reported that Aerococcus urinae is cotrimoxazole resistant. However, Aerococcus urinae can extract folate from the environment like Enterococcus using a high-affinity folate transport binding protein FolT. The thymidine or folate-containing culture media used to test the susceptibility may alter the result. In vivo, the folate concentration in the urine may depend upon the folate intake. Hence the outcome of the treatment with cotrimoxazole could be unpredictable. |
| Erythromycin, Clindamycin | Many strains are resistant |
| Fosfomycin Pivmecillinam | Many strains are resistant |