Antifungal
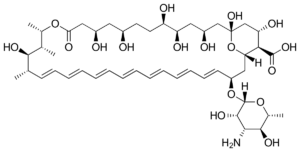
Ibrexafungerp: A novel antifungal
Ibrexafungerp, an enfumafungin derivative, belongs to a new family called triterpenoid antifungals.This is a new class called “-fungerp”. This antifungal class inhibits glucan synthetase required for fungal cell wall synthesis. One of the major antifungal class echinocandins also acts by this mechanism and has been used since 2001. Echinocandins, however, have poor bioavailability and are […]
Amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is a polyene antibiotic discovered in 1953 from the bacteria Streptomyces nodosus, in the Orinoco basin in Venezuela. Its name is derived from its amphoteric property, being able to react to both acid and base. It is insoluble at normal pH; hence it is available as a buffered colloidal solution, with sodium deoxycholate […]
Antifungals – Synergy, indifference and antagonism
A combination of antifungals is often used in cases of difficult-to-treat infections. What is the evidence in the literature about synergy, antagonism and indifference? Drug 1 Drug 2 Candida Aspergillus Cryptococcus neoformans Amphotericin B Echinocandin Indifference(survival – NA) Synergy, Indifference(Survival ↑) Synergy(survival – NA) Amphotericin B Flucytosine Synergy, indifference(Survival ↑) Synergy, indifference, antagonism(Survival ↑) Synergy, […]
Echinocandin
Echinocandins are a class of antifungals that prevent glucan synthesis pathways necessary for fungal cell wall formation. Echinocanins are antifungals that are widely used in clinical practice.Three echinocandins are approved for clinical use – Caspofungin, Micafungin and Anidulafungin.A fourth echinocandin – Rezafungin is being developed. Some other antifungals (some in development) that act of fungal cell walls […]