Virology
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (Presentation)
Respiratory Syncytial Virus is a single-stranded RNA virus with a negative sense, non-segmental RNA. It is an enveloped virus with many proteins, which help perform various functions like Attachment to the host cell, the fusion of host cell membranes, ion channels, viral assembly, RNA binding, transcription, phosphorylation, immune evasion etc. The virus may have a […]
Norovirus
Epidemiology Norovirus is the most common cause of epidemic gastroenteritis worldwide. In the UK, norovirus outbreak is usually seen in the winter months. The virus Norovirus is a small non-enveloped RNA virus of the caliciviridae family. It has ten genogroups, but I, II and IV are primarily implicated in human infection. Genogroup II is most […]
Infectious mononucleosis and Epstein-Barr Virus
Cause: Epidemiology: Transmission: Signs and symptoms: Complications Diagnosis If you want to know about a heterophile antibody, see this video. Atypical lymphocytes can also be seen in CMV, HIV, HHV6, rubella, mumps, viral hepatitis, toxoplasmosis, typhus, lead poisoning etc. Differential diagnosis: Treatment:
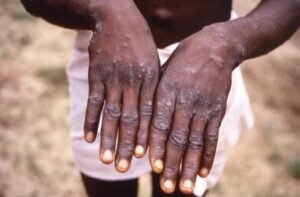
Human Monkeypox
Monkeypox is an emerging disease. It was first discovered in 1958 in a captive monkey population, from which it received its name. However, monkeys are not its main reservoir. The largest natural reservoir population is rodents. The full lifecycle and the extent of the reservoir population are still unknown.Monkeypox is a zoonosis. The virus: It […]
Adenovirus
Introduction For high-resolution images, scroll to the bottom of the page Human adenovirus has 7 species based on their haemagglutination character.Each species was divided into serotypes based on neutralisation (e.g. A- 12,18, 31). At present, genotyping is being used to classify Adenovirus.Different species of human adenovirus have different tissue tropism. Species Tissue tropism A GI, respiratory, […]
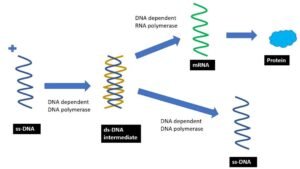
Virus – Baltimore classification
Baltimore classification - classification of viruses based on how they produce their mRNA.