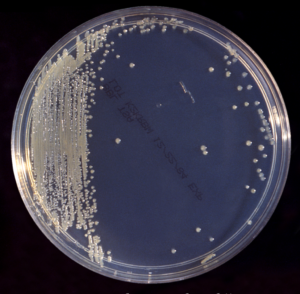
Cronobacter sakazakii: pathogen from infant formula feed
What is Cronobacter sakazakii? Cronobacter sakazakii is a gram-negative bacteria that can cause necrotising enterocolitis, septicaemia, and meningitis in infants, particularly low-birth-weight neonates. It has repeatedly been associated with reconstituted powdered infant formula. It can also cause infection in adults, especially in vulnerable groups like older people. Infection in infants is associated with a high […]
COVID vaccine
Age-specific recommendations on vaccine type Primary vaccination Based on the JCVI advice, the preference is to use the bivalent mRNA vaccines containing the latest variant (currently BA.4/5), however using a bivalent with a previous variant (such as BA.1) or full dose mRNAvaccine (Pfizer BioNTech 30 micrograms) may be used if there would otherwise be a […]
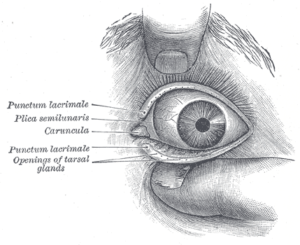
Corynebacterium macginleyi – an under-reported cause of conjunctivitis
Corynebacterium macginleyi (CM) is lipophilic, slow-growing, gram-positive bacteria first described in 1995 and was named after Kenneth McGinley, who made an essential contribution to the field of lipophilic coryneform bacteria. CM has been associated with conjunctivitis and other eye-related infections. It has also been implicated in various non-ophthalmic infections as an opportunistic pathogen. It has […]
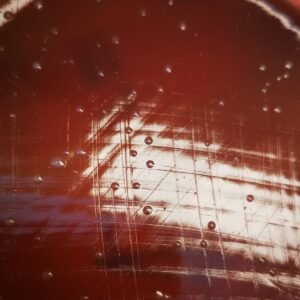
Catalase test
This test detects the catalase enzyme present in most cytochrome-containing aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria. The catalase enzyme converts hydrogen peroxide ( H2O2 ) to oxygen and water. This reaction can be observed as the rapid formation of bubbles. The reaction 2 H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2 Catalase positive organisms Gram-positive organisms Staphylococcus, Micrococcus,Aerococcus urinae (Note: Aerococcus […]
Cardiobacterium spp (C hominis, C valvarum)
Bacteria: Microaerophilic, pleomorphic gram-negative bacillus often with swelling of one or both ends and retained crystal violet dye at the poles.It is a part of the normal flora of the nose and throat. Culture and identification: Culture API 20NE – may misidentify it as Pasteurella.MALDI ToF16s rRNA PCR Clinical presentation: Antibiotic susceptibility: Variable susceptibility: Treatment is […]
Capnocytophaga spp.
Capnocytophaga genus belongs to the family Flavobacteriaceae.There are >9 species of Capnocytophaga, which can be divided into two groups – resident of human mouth flora and dog/cat mouth flora. Species found in the human oral cavity C. gingivalis, C. granulosa, C. haemolytica, C. leadbetteri, C. ochracea and C. sputigena Species found in dog/cat oral cavity C. canimorsus and C. cynodegmi Risk factors […]
Candida auris: an emerging multi-resistant fungus
Introduction Candida auris is a pathogen that has emerged as a global threat in recent years. It is the first human pathogenic fungus subject to international health alerts. The reason behind these concerns are – Public Health England reported in 2017 that almost all the C auris in the UK are fluconazole-resistant. There is also […]
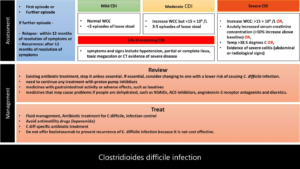
C difficile Infection guideline – comparison between NICE 2021 and IDSA 2021
What does NICE guideline 2021 say about assessing and managing C difficile infection? Comparison between NICE 2021 guideline and IDSA 2021 update IDSA/SHEA focussed update 2021 NICE 2021 1st episode of CDAD -1st line Fidaxomicin 200 mg BO PO 10 days Vancomycin 125 mg QDS PO 10 days 1st episode of CDAD - 2nd line […]
Brucella
Bacteria There are many Brucella species – not all known to cause human disease. Those known to cause human disease are – B melitensis, B abortus, B suis, B canis and B ceti. Brucella infection is a zoonosis – each Brucella sp is associated with some animal host – Brucella survives in the environment for […]
Aspergillus niger
The Fungus: Identification: It initially forms white colonies with a yellow back, which quickly becomes black. Conidia is rough, brownish-black, biseriate, and covers the entire vesicle. A key feature in diagnosing A. niger infection is the presence of calcium oxalate crystals on pathological examination. The presence of crystals can be taken as an indication of A niger […]