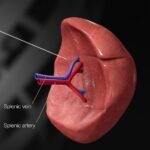
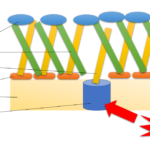
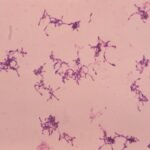
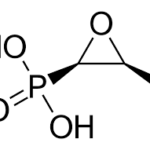
Trainee experience: Tips for part 1 FRCPath Microbiology
One of my trainees, who joined us as a year 1 infection trainee, recently passed part 1 FRCPath. I worked closely with him as a clinical supervisor. I asked him what tips he would give other trainees preparing for part 1. I think talking to you and looking at your Microregistrar and Facebook FRCPath blogs…