Antibiotic
Mechanism of resistance in Enterococcus
Enterococci are intrinsically resistant to many classes of antibiotics – like cephalosporins, Aminoglycoside (low-level resistance), macrolides, clindamycin, quinupristin-dalfopristin (E faecalis), Fusidic acid, Sulfonamide [EUCAST], which limits our options when we try to treat Enterococcal infections. Most clinical infections are caused by Enterococcus faecalis, followed by Enterococcus faecium.Other Enterococci occasionally isolated from the clinical specimen are […]
Antibiotic – intrinsic resistance
Microorganisms are only listed as “intrinsically resistant” to an agent (or group of agents) when a vast majority of wild-type isolates exhibit MIC values that are so high that the agent should not be considered for either therapy or clinical susceptibility testing (EUCAST). Enterobacterales & Aeromonas Enterobacterales and Aeromonas are intrinsically resistant to benzylpenicillin, glycopeptides, […]
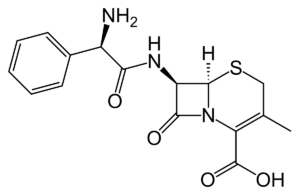
Cefalexin
Nature of the antibiotic Mechanism of action Cefalexin, like other beta-lactams, binds to the penicillin-binding protein (PBP) and prevents peptidoglycan synthesis. It prevents the formation of new cell walls and maintenance of the cell wall leading to autolysis of the bacteria due to osmotic pressure. Mechanism of resistance PK/PD and other properties Indication (cefalexin is […]
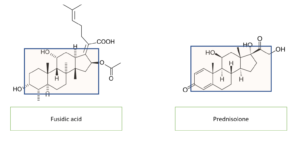
Fusidic acid
Fusidic acid was discovered in Copenhagen, Denmark and introduced to clinical practice in the 1960s.It was derived from a fungus, Fusidium coccineum. Fusidic acid has a structural similarity with the steroid molecule. You can see in the picture the molecular structure is similar to prednisolone. For this reason, it is called a steroid antibiotic. It also […]
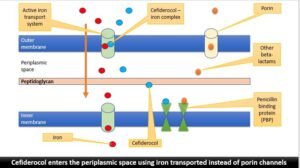
Cefiderocol
Cefiderocol, mechanism of action of cefiderocol, mechanism of resistance of cefiderocol, Use of cefiderocol