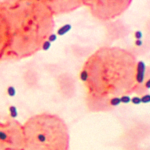
Metronidazole
Class: Nitroimidazole.Mol weight: 171First used in 1960. Mechanism of action: Metronidazole enters the susceptible (bacterial/parasite) cells by passive diffusion. It gets activated to a nitroso compound which causes oxidative damage to the DNA. It also inhibits DNA repair. The conversion of metronidazole to nitroso compound creates a concentration gradient, and more metronidazole enters the cells. The aerobic bacteria lack the necessary…
Quick observations on the exam (Part 1/CICE) – by a successful overseas candidate
2023 Spring exam experience: I have recently sat for this exam this Spring. My account is like this. I think everyone has different strengths and weaknesses and different learning styles so adapt it accordingly. For Part 1, we need to know bits and bobs about a lot of things. And there was not a time,…

Preparing for the FRCPath Part 1 Exam in Medical Microbiology and Virology
An IMG’s Perspective by Dr Chidi Onwukwe (2018) I decided to sit for the FRCPath part 1 in MMV sometime in 2018. I didn’t have a timeframe to work with as it was basically a loose decision made in a rare moment of inspiration. The first window of opportunity came in November/December 2018 in the…
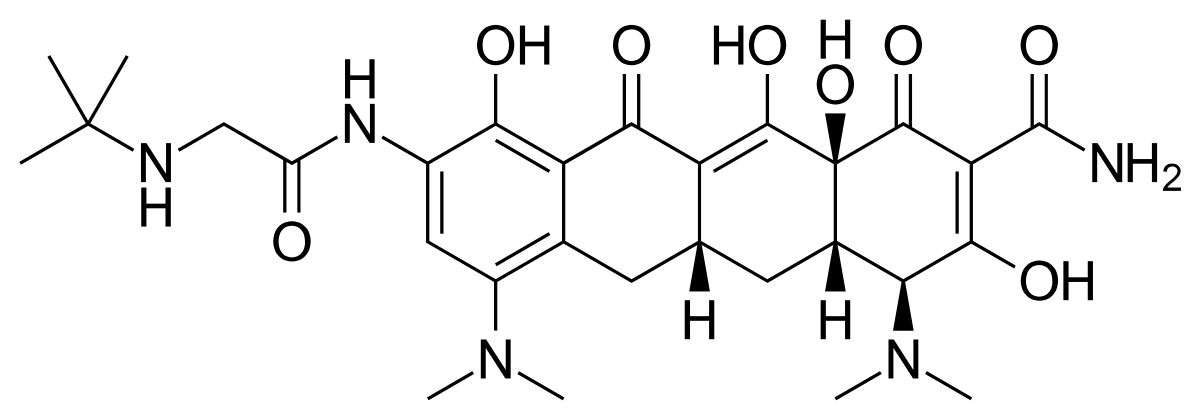
Tigecycline
Nature: Glycylcycline, a member of the tetracycline family. Semisynthetic derivative of minocycline.MW: 585.6 Mechanism of action: 1. Bind to 30S ribosomal subunit and inhibit protein synthesis – It inhibits the attachment of aminoacyl tRNA to the A site and prevents chain elongation, i.e. block the translation process.2. Inhibit mitochondrial protein synthesis by binding to 70…
Rotavirus vaccine (study note)
Vaccine Efficacy– Protect against gastroenteritis due to rotavirus serotypes G1P, G2P, G3P, G4P, and G9P; some efficacy against uncommon rotavirus genotypes G8P and G12P.– Over 85% effective at protecting against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis in the first two years of life. Administration of the vaccine Rotarix® should not be given to infants under 6 weeks of age.WHO recommends infants should…

Fusidic acid
Fusidic acid was discovered in Copenhagen, Denmark and introduced to clinical practice in the 1960s.It was derived from a fungus, Fusidium coccineum. Fusidic acid has a structural similarity with the steroid molecule. You can see in the picture the molecular structure is similar to prednisolone. For this reason, it is called a steroid antibiotic. It also…
Norovirus
Epidemiology Norovirus is the most common cause of epidemic gastroenteritis worldwide. In the UK, norovirus outbreak is usually seen in the winter months. The virus Norovirus is a small non-enveloped RNA virus of the caliciviridae family. It has ten genogroups, but I, II and IV are primarily implicated in human infection. Genogroup II is most…
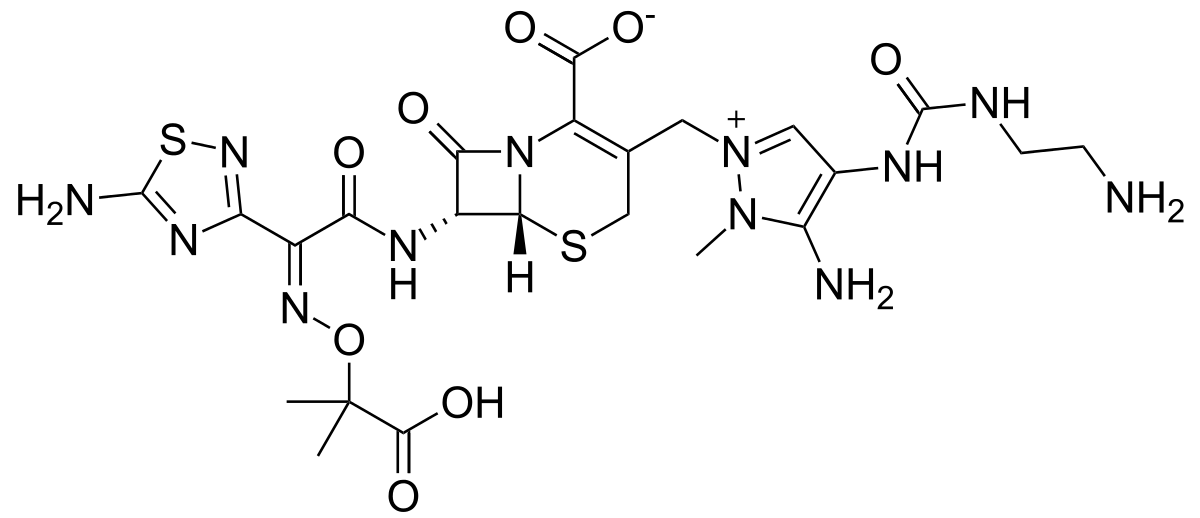
Ceftolozane-tazobactam
Class: 5th generation cephalosporin.Available as ceftolozane-tazobactam, a beta lactam-beta lactamase inhibitor (BLBLI) combination. Mechanism of Action: Similar to other beta-lactam antibiotics. It binds to the penicillin-binding protein (PBP) to inhibit the biosynthesis of the cell wall.It binds with the PBP3 of E coli and PBP3, PBP1a, and PBP1b of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mechanism of resistance: It is…
NICE Guidelines and other documents – Infection
Check the most recent updates here:https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/conditions-and-diseases/infections/covid19/products?Status=Published